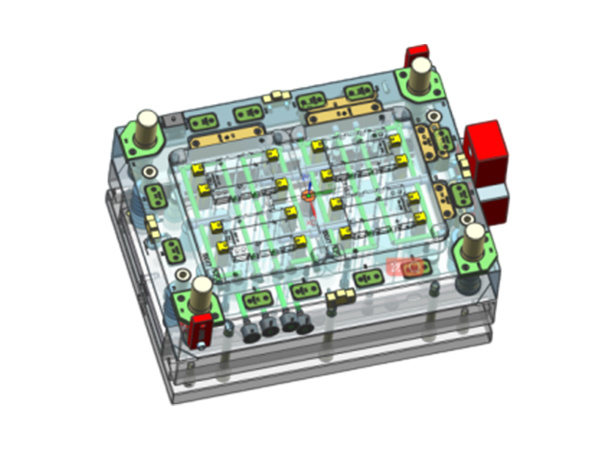
Optimizing Injection Molds for Air Intake Pipe Assembly: A Comprehensive Guide
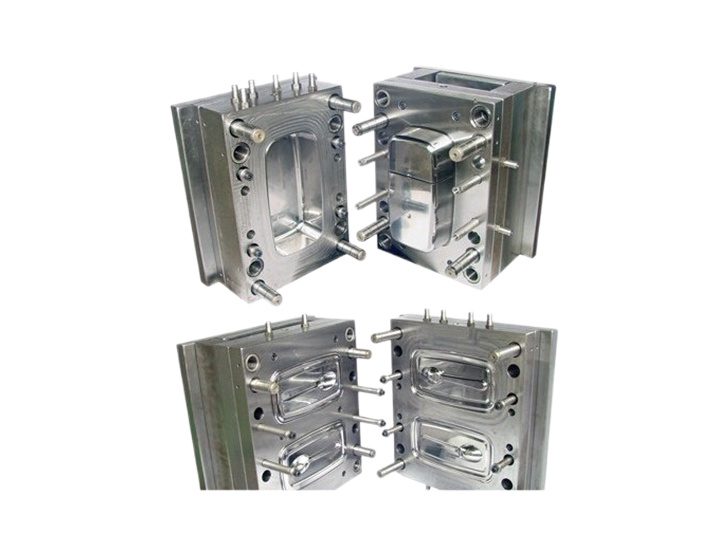
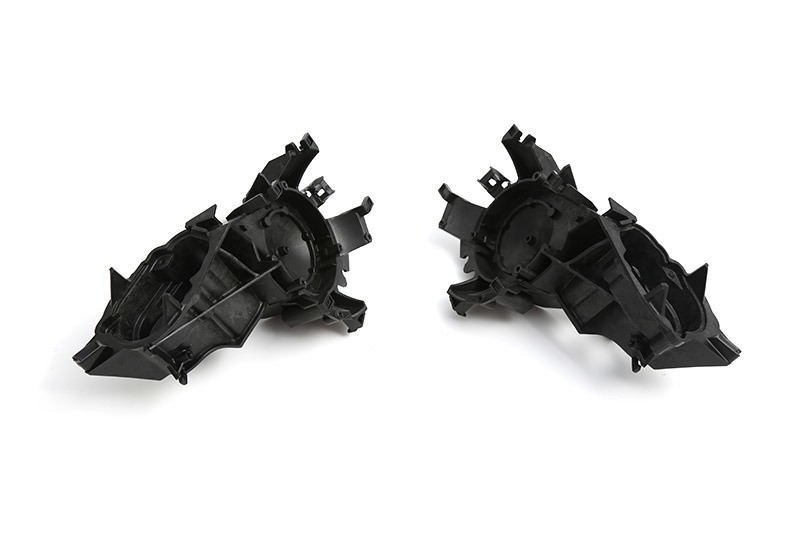
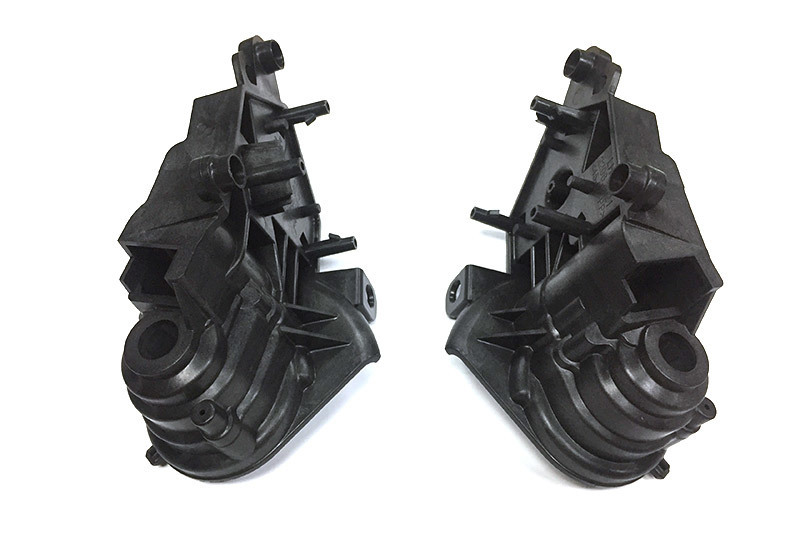
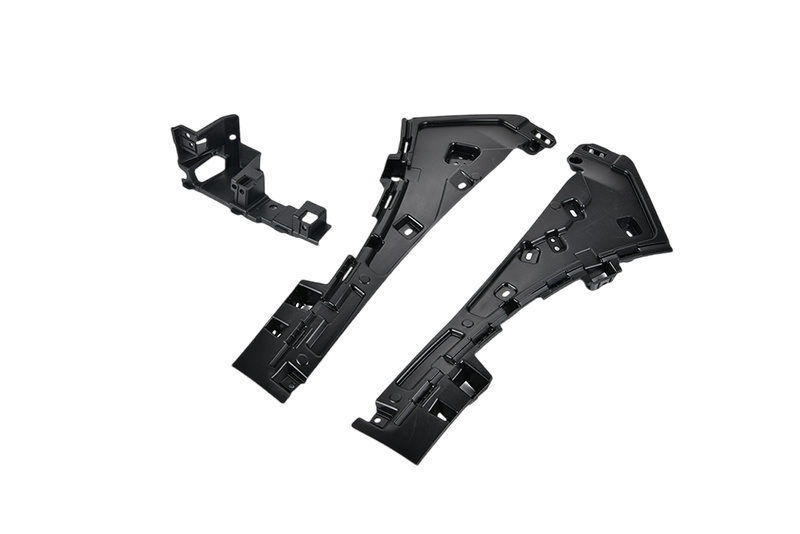
Injection molding is a pivotal process in the manufacturing of various components, including air intake pipe assemblies. The design and optimization of injection molds for such applications play a crucial role in ensuring high-quality production and operational efficiency. An air intake pipe assembly serves as a critical component in automotive applications, directing airflow into the engine to en
2026-01-30
Injection molding is a pivotal process in the manufacturing of various components, including air intake pipe assemblies. The design and optimization of injection molds for such applications play a crucial role in ensuring high-quality production and operational efficiency. An air intake pipe assembly serves as a critical component in automotive applications, directing airflow into the engine to enhance performance and efficiency. Therefore, developing an effective injection mold is essential to meet stringent automotive industry standards.
One of the primary considerations in creating injection molds for air intake pipe assemblies is the selection of materials. The materials used in both the mold and the final product must be carefully chosen to withstand the rigors of heat and pressure while providing adequate strength and durability. Commonly used materials for molding include ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon, each offering distinct advantages based on the specific requirements of the air intake system.
Design considerations are equally important in the injection mold process. For air intake pipes, mold designs must account for factors such as wall thickness, draft angles, and gate locations. Uniform wall thickness is crucial to prevent warping during cooling, while appropriate draft angles facilitate easier part ejection and reduce the risk of damage during removal. Additionally, the placement of gates can significantly impact the flow of molten plastic and, consequently, the quality of the finished product. Proper flow management helps minimize defects, such as sink marks or voids.
Furthermore, the cooling system within the injection mold must be optimized to ensure efficient temperature control during the molding process. Effective cooling reduces cycle times, enhances dimensional stability, and improves overall product quality. Implementing conformal cooling channels can further enhance cooling efficiency, ensuring that the mold maintains a uniform temperature throughout the production cycle.
Another critical aspect of injection mold design for air intake pipe assemblies is the incorporation of features that facilitate assembly and integration into larger systems. This might involve designing snap-fit features or alignment aids that simplify the installation process. Such considerations not only improve the functionality of the final product but also enhance the assembly process, resulting in reduced labor costs and improved overall efficiency.
In conclusion, the optimization of injection molds for air intake pipe assemblies requires a multifaceted approach, considering material properties, design intricacies, cooling efficiency, and assembly features. By focusing on these key areas, manufacturers can achieve high-quality, efficient, and reliable production of air intake components that meet the demands of the automotive industry. Continuous advancements in mold design and technology will further enhance the capabilities of injection molding, paving the way for innovative solutions in manufacturing.
One of the primary considerations in creating injection molds for air intake pipe assemblies is the selection of materials. The materials used in both the mold and the final product must be carefully chosen to withstand the rigors of heat and pressure while providing adequate strength and durability. Commonly used materials for molding include ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon, each offering distinct advantages based on the specific requirements of the air intake system.
Design considerations are equally important in the injection mold process. For air intake pipes, mold designs must account for factors such as wall thickness, draft angles, and gate locations. Uniform wall thickness is crucial to prevent warping during cooling, while appropriate draft angles facilitate easier part ejection and reduce the risk of damage during removal. Additionally, the placement of gates can significantly impact the flow of molten plastic and, consequently, the quality of the finished product. Proper flow management helps minimize defects, such as sink marks or voids.
Furthermore, the cooling system within the injection mold must be optimized to ensure efficient temperature control during the molding process. Effective cooling reduces cycle times, enhances dimensional stability, and improves overall product quality. Implementing conformal cooling channels can further enhance cooling efficiency, ensuring that the mold maintains a uniform temperature throughout the production cycle.
Another critical aspect of injection mold design for air intake pipe assemblies is the incorporation of features that facilitate assembly and integration into larger systems. This might involve designing snap-fit features or alignment aids that simplify the installation process. Such considerations not only improve the functionality of the final product but also enhance the assembly process, resulting in reduced labor costs and improved overall efficiency.
In conclusion, the optimization of injection molds for air intake pipe assemblies requires a multifaceted approach, considering material properties, design intricacies, cooling efficiency, and assembly features. By focusing on these key areas, manufacturers can achieve high-quality, efficient, and reliable production of air intake components that meet the demands of the automotive industry. Continuous advancements in mold design and technology will further enhance the capabilities of injection molding, paving the way for innovative solutions in manufacturing.
Related news