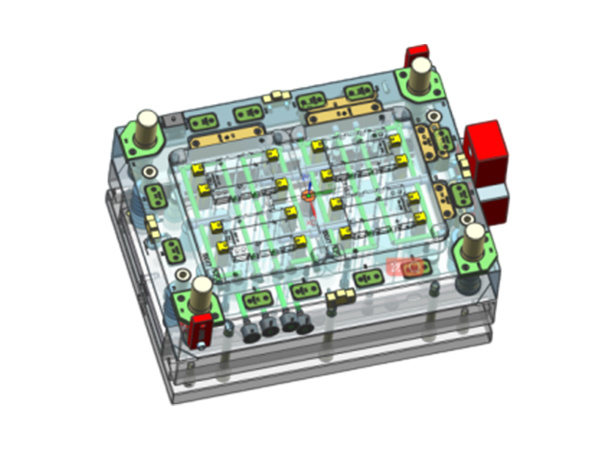
Understanding Injection Molding for Drain Trays: A Comprehensive Guide
Injection molding is a widely utilized manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to form specific shapes. When it comes to producing drain trays, this method offers several advantages, including high efficiency, consistent quality, and the ability to create complex geometries. Understanding the key aspects of injection molding for drain trays can significantly enhan
2026-01-14
Injection molding is a widely utilized manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to form specific shapes. When it comes to producing drain trays, this method offers several advantages, including high efficiency, consistent quality, and the ability to create complex geometries. Understanding the key aspects of injection molding for drain trays can significantly enhance the outcome of your manufacturing process.
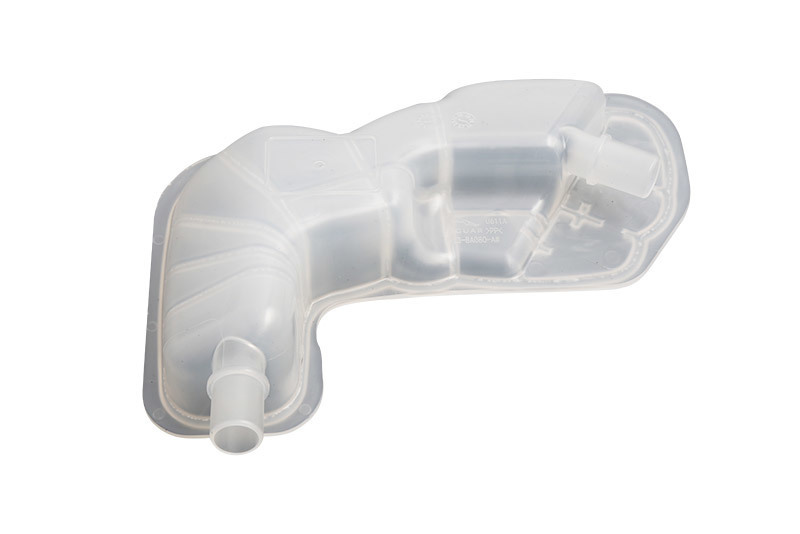
First and foremost, the material selection is critical in the injection molding process for drain trays. Commonly used materials include various types of plastics such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Each material has its own unique properties, such as chemical resistance, durability, and flexibility, making it essential to choose one that aligns with the intended use of the drain tray. For instance, if the tray is expected to hold water or other liquids, selecting a material with excellent water resistance and structural integrity is paramount.
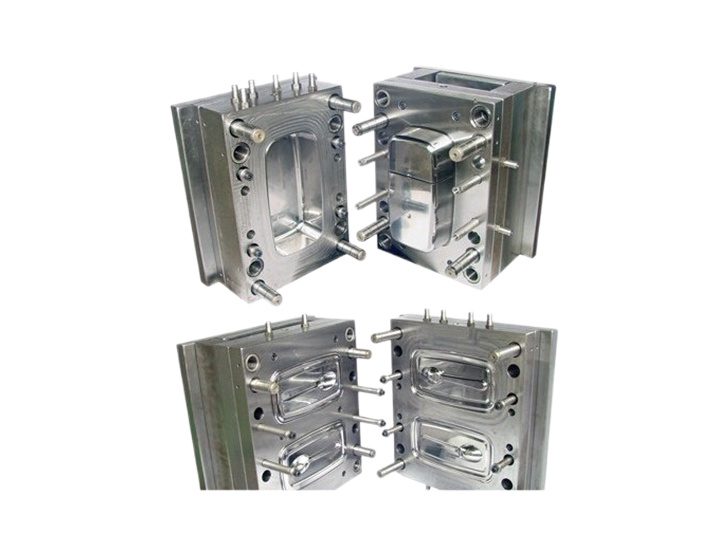
The design of the injection mold itself is another crucial factor in the success of manufacturing drain trays. The mold must be designed with precision to ensure proper flow of the molten material and to facilitate easy ejection of the finished product. Additionally, incorporating features such as drainage channels, ribs for added strength, and aligning the mold's release angles can enhance the functionality of the drain trays while reducing the risk of defects during production.
Temperature control during the injection molding process is also vital. The molten material must be heated to a specific temperature to achieve the right viscosity for injection. Once injected, the mold must be kept at an optimal temperature to allow for proper cooling and solidification. Inadequate temperature control can result in issues such as warping, incomplete filling, or surface imperfections.
Furthermore, the injection molding cycle time plays a significant role in determining production efficiency. A well-optimized cycle time ensures that each drain tray is produced quickly without compromising quality. Factors influencing cycle time include the complexity of the mold design, the type of material used, and the cooling time required for solidification.
Lastly, post-molding processes such as trimming, surface finishing, and quality inspection are essential steps that cannot be overlooked. These processes help in achieving the desired aesthetic and functional properties of the drain trays, ensuring they meet industry standards.
In conclusion, injection molding for drain trays is a multifaceted process that demands careful consideration of materials, mold design, temperature control, cycle time, and post-molding finishing. By understanding these elements, manufacturers can optimize their production processes and deliver high-quality drain trays that meet the needs of their customers.
First and foremost, the material selection is critical in the injection molding process for drain trays. Commonly used materials include various types of plastics such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Each material has its own unique properties, such as chemical resistance, durability, and flexibility, making it essential to choose one that aligns with the intended use of the drain tray. For instance, if the tray is expected to hold water or other liquids, selecting a material with excellent water resistance and structural integrity is paramount.
The design of the injection mold itself is another crucial factor in the success of manufacturing drain trays. The mold must be designed with precision to ensure proper flow of the molten material and to facilitate easy ejection of the finished product. Additionally, incorporating features such as drainage channels, ribs for added strength, and aligning the mold's release angles can enhance the functionality of the drain trays while reducing the risk of defects during production.
Temperature control during the injection molding process is also vital. The molten material must be heated to a specific temperature to achieve the right viscosity for injection. Once injected, the mold must be kept at an optimal temperature to allow for proper cooling and solidification. Inadequate temperature control can result in issues such as warping, incomplete filling, or surface imperfections.
Furthermore, the injection molding cycle time plays a significant role in determining production efficiency. A well-optimized cycle time ensures that each drain tray is produced quickly without compromising quality. Factors influencing cycle time include the complexity of the mold design, the type of material used, and the cooling time required for solidification.
Lastly, post-molding processes such as trimming, surface finishing, and quality inspection are essential steps that cannot be overlooked. These processes help in achieving the desired aesthetic and functional properties of the drain trays, ensuring they meet industry standards.
In conclusion, injection molding for drain trays is a multifaceted process that demands careful consideration of materials, mold design, temperature control, cycle time, and post-molding finishing. By understanding these elements, manufacturers can optimize their production processes and deliver high-quality drain trays that meet the needs of their customers.
Related news