Innovative Solutions: How Two Shot Molding Transforms Automotive Electronics
Innovative Solutions: How Two Shot Molding Transforms Automotive Electronics Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Two Shot Molding 2. What is Two Shot Molding? 3. Benefits of Two Shot Molding in Automotive Electronics - a. Cost Efficiency - b. Enhanced Durability - c. Design Flexibility 4. Applications of Two Shot Molding in Automotive Electronics - a. Sensor Housings
2025-08-10
Innovative Solutions: How Two Shot Molding Transforms Automotive Electronics
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Two Shot Molding
2. What is Two Shot Molding?
3. Benefits of Two Shot Molding in Automotive Electronics
- a. Cost Efficiency
- b. Enhanced Durability
- c. Design Flexibility
4. Applications of Two Shot Molding in Automotive Electronics
- a. Sensor Housings
- b. Dashboards and Control Panels
5. The Two Shot Molding Manufacturing Process
6. Environmental Impact of Two Shot Molding
7. The Future of Automotive Electronics with Two Shot Molding
8. Frequently Asked Questions
9. Conclusion
Introduction to Two Shot Molding
In an era where automotive technology is advancing at a rapid pace, the need for innovative manufacturing techniques has never been more critical. **Two-shot molding** has emerged as a transformative process that significantly enhances the production of automotive electronics. This innovative technique enables manufacturers to create complex components with multiple materials in a single cycle, improving both functionality and efficiency.
What is Two Shot Molding?
**Two-shot molding**, also known as **dual-shot molding**, is a manufacturing process that involves injecting two different thermoplastic materials into a single mold to create a finished component. This method allows for the integration of multiple features into a single part, which traditionally would require separate components. By utilizing this innovative approach, manufacturers can achieve better adhesion, improved aesthetics, and enhanced performance characteristics.
The process begins with the injection of the first material into the mold, followed by the introduction of a second material, which can be of a different color, texture, or functionality. The two materials bond during the molding cycle, resulting in a single cohesive part that exhibits the properties of both materials.
Benefits of Two Shot Molding in Automotive Electronics
The advantages of two-shot molding are numerous, especially in the context of automotive electronics. Below, we delve into some of the most significant benefits associated with this innovative process.
Cost Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of two-shot molding is its **cost efficiency**. By combining multiple processes into one, manufacturers can significantly reduce labor and production costs. The streamlined approach eliminates the need for secondary assembly operations, which can be time-consuming and expensive. Furthermore, the reduction in waste generated during manufacturing further contributes to cost savings, making two-shot molding an economically attractive option for automotive producers.
Enhanced Durability
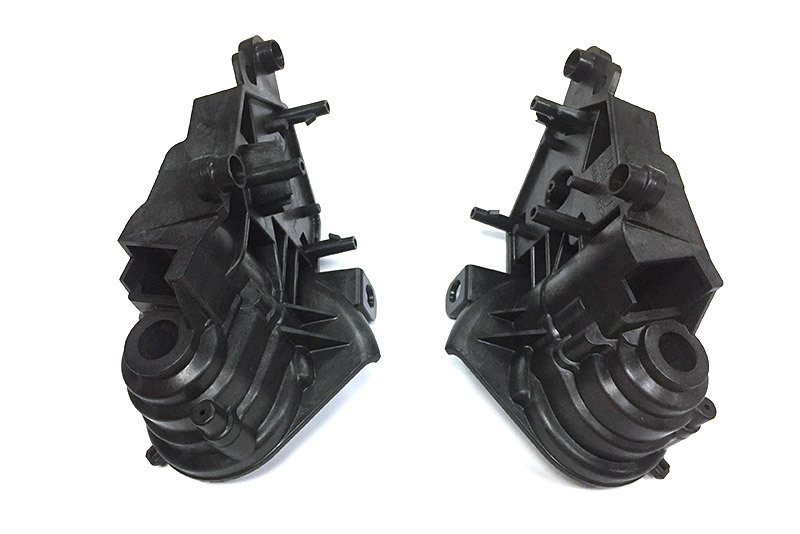
Automotive components must withstand harsh conditions, including temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and exposure to chemicals. Two-shot molding enhances the **durability** of automotive electronics by allowing manufacturers to use materials with complementary properties. For instance, a hard outer shell can provide impact resistance, while a softer inner layer can offer flexibility and insulation against electrical hazards. This combination results in components that are not only robust but also reliable over an extended lifecycle.
Design Flexibility
The **design flexibility** afforded by two-shot molding is unparalleled. Designers can integrate multiple functionalities into a single component, thereby optimizing space within vehicles. This ability to create intricate designs with varying textures, colors, and functionalities in one shot leads to innovative product designs that enhance user experience. For example, control panels can feature tactile surfaces combined with visual aesthetics, making them more user-friendly while maintaining high performance.
Applications of Two Shot Molding in Automotive Electronics
Two-shot molding has a wide range of applications in the field of automotive electronics. Below, we explore some of these applications, highlighting the versatility and effectiveness of this manufacturing technique.
Sensor Housings
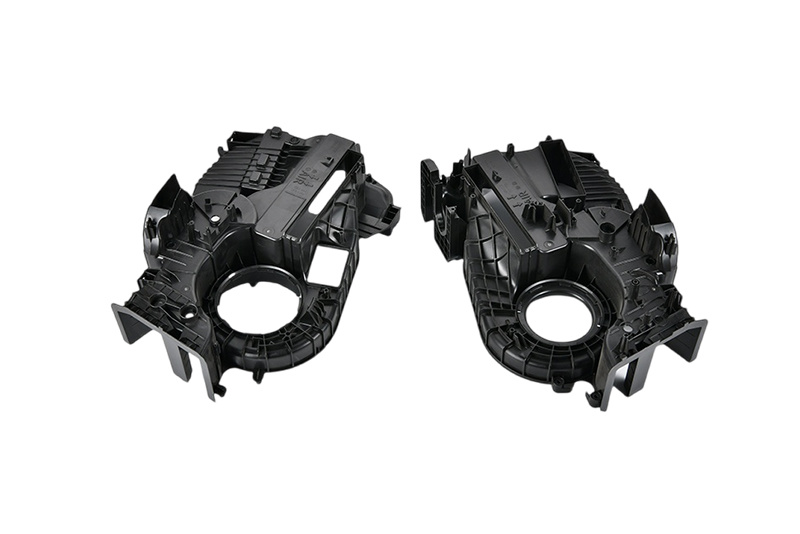
Sensor housings are critical components in modern vehicles, responsible for protecting delicate electronic sensors from environmental factors. Two-shot molding allows manufacturers to create robust housings that can withstand harsh conditions while providing a snug fit for the sensors. The use of different materials can enhance sealing properties, ensuring that sensors remain functional over time.
Dashboards and Control Panels
The automotive dashboard is a key interface between the driver and the vehicle's systems. Two-shot molding enables manufacturers to produce dashboards and control panels that are not only visually appealing but also functional. Complex designs can incorporate soft-touch materials for comfort and hard plastics for durability, all within a single molded part. This integration simplifies assembly and enhances the overall user experience.
The Two Shot Molding Manufacturing Process
Understanding the manufacturing process of two-shot molding is essential for appreciating its advantages. The process can be broken down into several key steps:
1. **Mold Design**: The process begins with creating a mold that can accommodate two different materials. The mold must be designed to allow for seamless transitions between the two materials while ensuring proper bonding.
2. **First Injection**: The first material is injected into the mold, filling the designated cavities. This initial step sets the foundation for the final product.
3. **Cooling and Solidification**: The first material is allowed to cool and solidify partially, creating a stable base for the second injection.
4. **Second Injection**: The second material is injected into the mold, surrounding the first material. This step requires precision to ensure that the two materials bond effectively.
5. **Final Cooling and Ejection**: The part is cooled again to solidify the second material fully. Once complete, the finished product is ejected from the mold.
This process can be repeated for various designs, allowing for the production of complex automotive electronic components efficiently.
Environmental Impact of Two Shot Molding
The environmental sustainability of automotive manufacturing is a growing concern, and two-shot molding presents several advantages in this regard. The process generates less waste compared to traditional methods as it minimizes the need for additional assembly and materials. Furthermore, manufacturers can select environmentally friendly materials, thus reducing the overall carbon footprint of production. As the automotive industry shifts towards sustainability, two-shot molding stands out as a forward-thinking solution.
The Future of Automotive Electronics with Two Shot Molding
As the automotive sector continues to evolve, the role of two-shot molding in automotive electronics is expected to expand significantly. This manufacturing process will likely play a crucial role in the development of next-generation vehicles, especially with the ongoing integration of advanced technologies such as **autonomous driving systems** and **smart connectivity**.
The demand for more complex electronic systems will drive innovation in two-shot molding, leading to the creation of components that are not only more sophisticated but also more reliable. Manufacturers who adopt this technique will be well-positioned to stay ahead of industry trends and meet the growing consumer expectations for high-quality automotive electronics.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What types of materials can be used in two-shot molding?
Two-shot molding can utilize a variety of thermoplastic materials, including polycarbonate, ABS, and TPU. The choice of materials depends on the desired properties of the final product.
2. How does two-shot molding compare to traditional injection molding?
Two-shot molding allows for the creation of complex parts with multiple materials in a single process, reducing assembly time and improving bonding. Traditional injection molding, on the other hand, typically involves single-material parts that may require additional assembly steps.
3. What are some challenges associated with two-shot molding?
Challenges can include mold design complexity, material compatibility, and the need for precise control over injection parameters to ensure proper bonding between materials.
4. Is two-shot molding suitable for high-volume production?
Yes, two-shot molding is highly suitable for high-volume production as it allows manufacturers to produce large quantities of complex parts efficiently.
5. How does two-shot molding contribute to automotive safety?
By enabling the creation of durable, integrated components, two-shot molding enhances the reliability of automotive electronics, which is crucial for safety-critical systems such as sensors and control panels.
Conclusion
Two-shot molding represents a significant advancement in the manufacturing of automotive electronics, offering numerous benefits including cost efficiency, enhanced durability, and design flexibility. As the automotive industry continues to embrace innovation, this technique will play a vital role in the development of new technologies and smarter vehicles. By understanding and leveraging the advantages of two-shot molding, manufacturers can position themselves at the forefront of the automotive electronics revolution, ensuring they meet the demands of a rapidly evolving market.
Related news